Microsoft Unveils AI‑Powered “Agentic OS” with Taskbar Integration
Key Points
- AI agents are now accessible directly from the Windows taskbar.
- Taskbar icons display real‑time status and allow users to monitor agent activity.
- The feature is optional and can be enabled or disabled by the user.
- Developers can use the Model Context Protocol to build secure, interoperable agents.
- Agents run in isolated workspaces to protect the main Windows environment.
- Copilot is integrated into File Explorer for document summarization and email drafting.
- Click to Do converts on‑screen tables into editable Excel spreadsheets.
- Writing assistance, Outlook summaries, and fluid dictation enhance productivity.
- Future updates include hardware‑accelerated BitLocker and Sysmon security tools.
- Passkey manager integration will work with major password‑manager services.
Microsoft is transforming Windows into an “agentic OS” by embedding AI agents directly into the Windows taskbar. The new capabilities let users launch Microsoft 365 Copilot and third‑party agents from the taskbar, monitor their progress, and receive notifications when tasks are completed. Developers gain a standardized framework for building agents that can access tools and other agents securely. Additional AI features are being rolled out across Windows, including Copilot integration in File Explorer, writing assistance, Outlook summaries, and a fluid dictation tool. The rollout is opt‑in, giving users control over their AI experience.
AI Agents Integrated Into the Taskbar
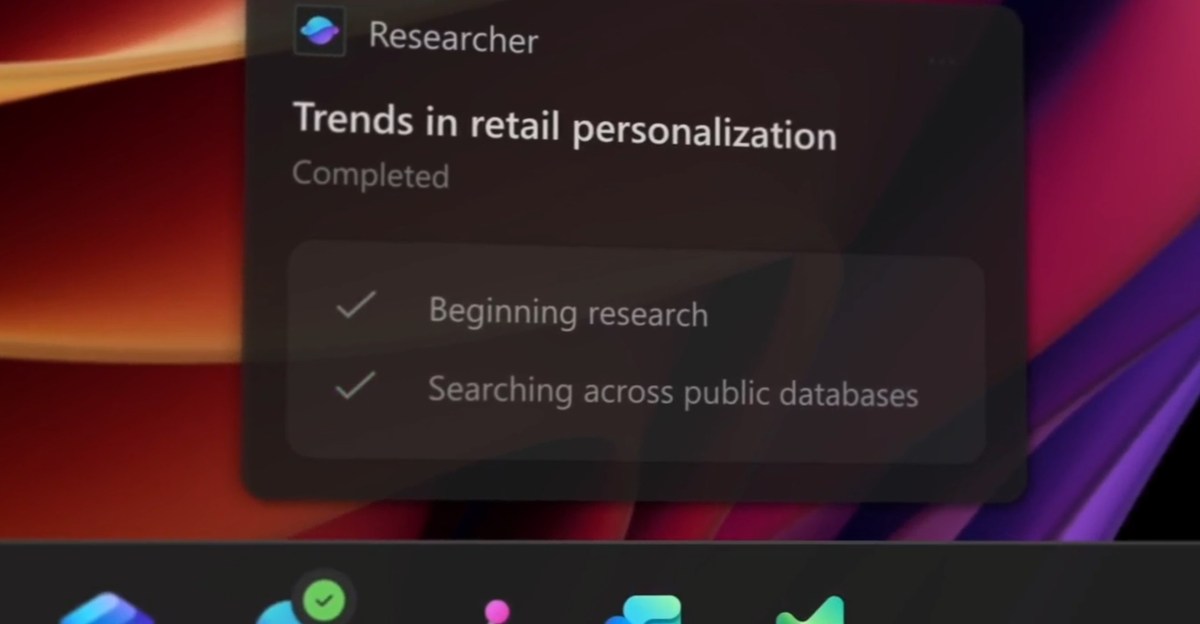
Microsoft is embedding artificial‑intelligence agents directly into the Windows taskbar, positioning the operating system as an “agentic OS.” Users can launch Microsoft 365 Copilot and a range of third‑party agents from a new taskbar icon. Once activated, an agent can run in the background, performing tasks such as researching data, accessing files, or automating repetitive administrative work. The taskbar shows real‑time status indicators: a visual badge signals when an agent needs attention, and a different badge confirms task completion. Hovering over the icon reveals a floating window that provides details about the agent’s activity.
The feature is optional; users can enable or disable it according to their preferences, ensuring full control over when and how AI assistance is employed.
Developer Platform and Secure Execution
Microsoft is providing developers with a standardized framework called the Model Context Protocol. This protocol enables agents to discover tools, interact with other agents, and operate within a secure, managed on‑device registry. Each agent runs in its own workspace, isolated from the main Windows session, creating a policy‑controlled environment that audits execution. This sandboxed approach enhances security while allowing agents to perform complex operations safely.
Broader AI Enhancements Across Windows
Beyond the taskbar, the company is extending AI functionality throughout the Windows experience. Copilot is being added to File Explorer, allowing users to summarize documents, answer questions about files, and draft emails directly from the file view. A feature called Click to Do lets users convert tables found anywhere on the PC into Excel spreadsheets, supporting both local and cloud‑based AI models. Writing assistance previews let users rewrite and compose text in any text box, with offline support on specific hardware.
Additional AI tools include Outlook‑generated summaries, automatic alt‑text generation for images in Word, and a fluid dictation feature that turns spoken input into grammatically correct text. Windows 365 cloud PCs also receive these AI capabilities, blending local and cloud‑based Copilot features.
Future Outlook and Additional Features
Microsoft’s roadmap includes hardware‑accelerated security features such as BitLocker support that will activate when compatible silicon becomes available. System monitoring functionality, referred to as Sysmon, is slated for early integration, simplifying security event logging. The visual design of Windows Hello is being refreshed, and a passkey manager will integrate with popular password managers, enhancing authentication across the platform.
Overall, Microsoft’s push to integrate AI agents throughout the Windows ecosystem aims to provide users with powerful, context‑aware assistance while maintaining security and user control.