Google Enhances AI Mode with Visual Search Capabilities
Key Points
- Google adds visual search to its Gemini‑powered AI Mode, merging Image Search and Google Lens.
- Users can upload photos and ask conversational questions, receiving related images and product data.
- The system breaks images into objects, background, color and texture, running parallel internal queries.
- Results are recombined to match user intent, but may misinterpret queries or favor well‑optimized visuals.
- Integration with the Shopping Graph provides price, review and availability info for items in photos.
- Competitors like Pinterest Lens and Bing visual search exist, but few combine a global product database with conversational AI.
- Potential risks include bias, sponsorship elevation, and reduced visibility for sites lacking a visual presence.
Google has expanded its Gemini‑powered AI Mode by integrating visual search features drawn from Google Lens and its Image Search technology. Users can now upload photos and ask conversational questions about the content, receiving related images, product details, and contextual information. The new system breaks images into objects, background, color and texture, runs multiple internal queries in parallel, and recombines results that best match user intent. By linking to the Google Shopping Graph, which indexes billions of products, the feature also delivers price, review and availability data for items depicted in photos. While the upgrade promises a more natural, image‑centric search experience, Google acknowledges potential misinterpretations, bias, and the risk that sites lacking optimized visuals may be underrepresented.
Visual Search Joins Gemini‑Powered AI Mode
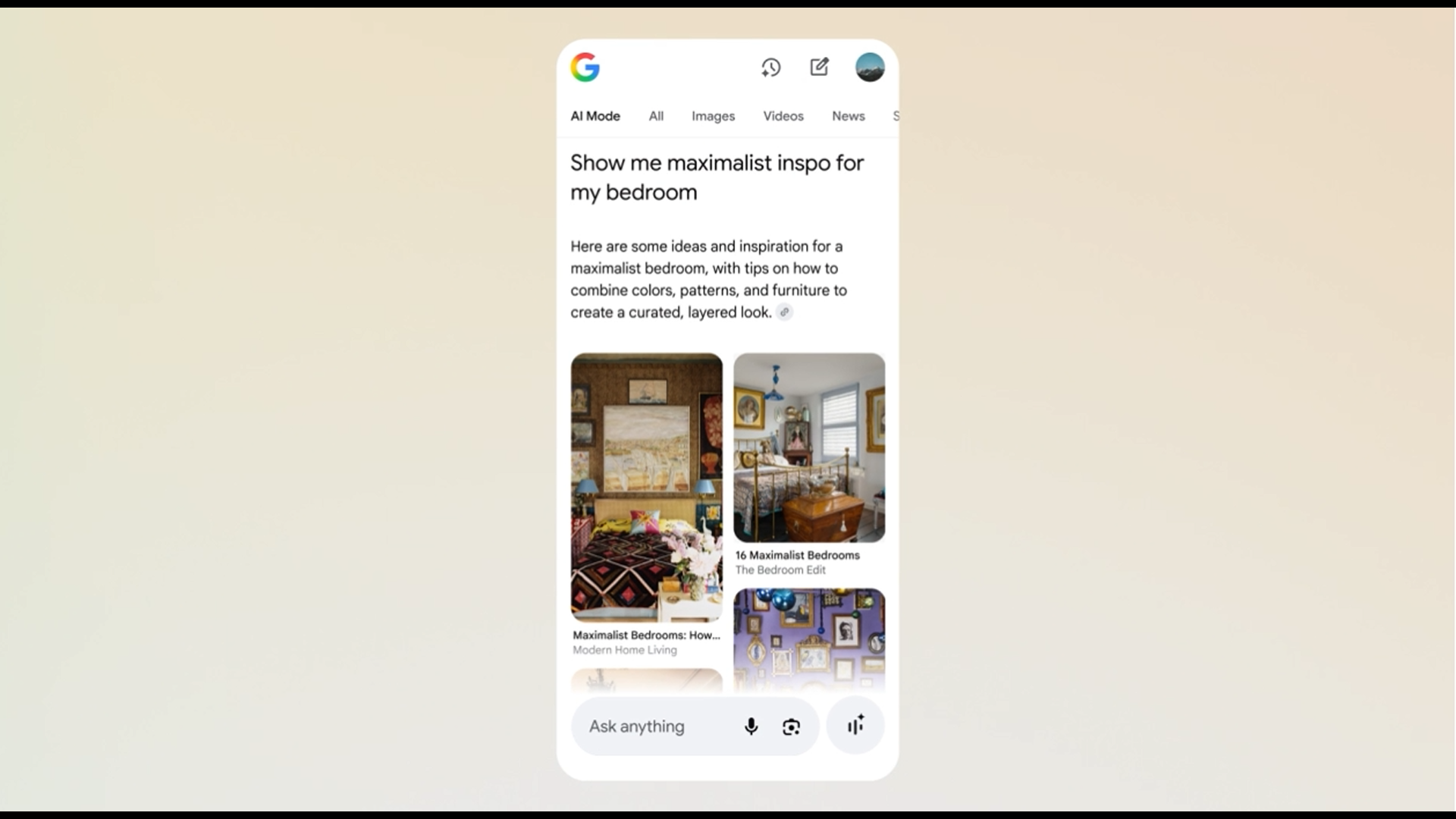
Google has introduced a visual dimension to its Gemini‑driven AI Mode, blending traditional text‑based search with the capabilities of Google Lens and Image Search. The enhancement lets users upload a photograph and ask natural‑language questions about it, or receive collections of images that align with the original query. Examples described in the announcement include asking the system to show a fashion style in lighter shades or to explore retro 1950s living‑room designs based on a single snapshot.
How the Visual Engine Works
The visual component employs what Google calls a “visual search fan‑out” approach layered on top of the existing fan‑out method used for textual queries. When a user provides an image, the system decomposes it into distinct elements—objects, background, color and texture—and dispatches multiple internal queries concurrently. This parallel querying allows the engine to retrieve a broader set of relevant images, rather than merely echoing the original picture. The returned results are then recombined, prioritizing those that best satisfy the user’s intent.
Implications for Search Results
Google’s search infrastructure must decide which of the retrieved visuals to spotlight and which to suppress. The company notes that the system could misread intent, elevate sponsored content, or favor large brands whose visual assets are better optimized for AI consumption. Consequently, websites lacking clean imagery or robust visual metadata risk diminished visibility in the new visual‑centric results.
Integration with the Shopping Graph
On the commerce side, the visual search leverages Google’s Shopping Graph, a massive index that catalogues billions of products and updates hourly. A photo of a pair of jeans, for instance, can surface current pricing, consumer reviews and local store availability in a single flow. This capability aims to turn vague visual prompts into concrete shopping options, simplifying the path from discovery to purchase.
Competitive Landscape
Google’s move places it alongside existing visual search tools such as Pinterest Lens and Microsoft’s Copilot‑enabled Bing visual search. However, the company argues that few competitors combine a global product database, live price data and conversational AI in a single offering. By merging these elements, Google hopes to set a new baseline for search experiences that are as much about seeing as reading.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Despite the promise, Google acknowledges possible pitfalls. Misinterpretations of user intent, inaccurate or biased visual results, and the inadvertent promotion of sponsored items could erode trust. If the system fails to deliver reliable answers, users may revert to traditional keyword searches or turn to niche applications that specialize in particular visual domains.
Looking Forward
The introduction of visual search into AI Mode reflects a broader industry shift toward more tactile, image‑driven interactions. As devices become better at sensing and describing the world around them, search engines are evolving to understand not just words but also what users see. Google’s expansive infrastructure gives it a substantial head start, but the ultimate success of the feature will hinge on its accuracy, fairness and usefulness in everyday queries.